Description
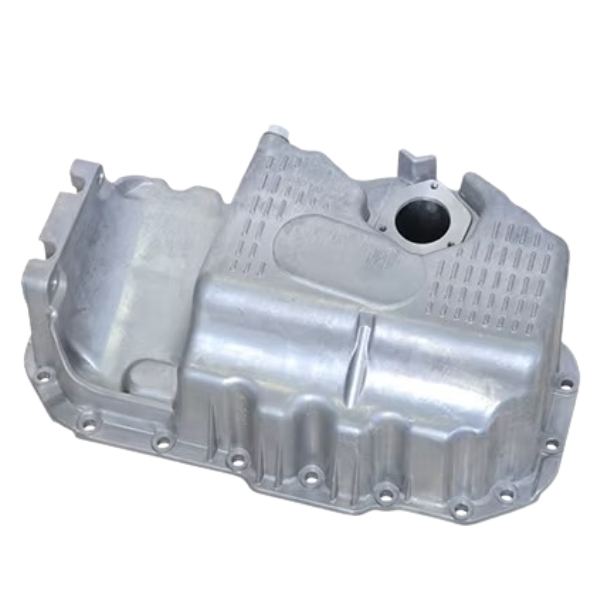
Get VW Golf V 1.6 FSI Oil Sump 03C103603S in Kenya
The oil sump, also known as the oil pan, is a critical component of an internal combustion engine. It serves as a reservoir for engine oil, ensuring that the engine remains lubricated and operates smoothly. In this comprehensive discussion, we will explore the function of the oil sump, its importance, different types, potential issues, maintenance practices, and overall impact on engine performance.
1. What is an Oil Sump?
The oil sump is a large, usually metal container located at the bottom of the engine block. It collects and holds engine oil after it has circulated through the engine to lubricate the various moving parts. The oil sump is designed to accommodate the volume of oil needed for effective lubrication, and it plays a key role in the oil circulation system.
2. Function of the Oil Sump
A. Oil Reservoir
The primary function of the oil sump is to serve as a reservoir for engine oil. When the engine is running, the oil pump draws oil from the sump and circulates it through the engine. This oil lubricates the moving parts, reducing friction and preventing wear and tear.
B. Cooling the Oil
As the engine operates, the oil absorbs heat from various components. The oil sump helps dissipate some of this heat, allowing the oil to cool down before it is recirculated. This cooling effect is crucial for maintaining the oil’s viscosity and performance.
C. Filtration of Contaminants
The oil sump also plays a role in filtering out contaminants. As the oil circulates through the engine, it picks up dirt, debris, and metal particles. These contaminants settle at the bottom of the sump, allowing the oil to remain cleaner for a more extended period.
D. Oil Level Indicator
The oil sump often includes a dipstick or an oil level sensor that allows for monitoring the oil level. This feature is essential for maintaining the proper oil level in the engine, ensuring optimal lubrication and performance.
3. Importance of the Oil Sump
A. Engine Lubrication
The oil sump is vital for ensuring proper engine lubrication. Without sufficient oil, engine parts would experience increased friction, leading to overheating and potentially catastrophic failure. The oil sump provides a steady supply of oil to maintain the necessary lubrication.
B. Engine Protection
By acting as a reservoir for oil, the sump protects the engine from premature wear and damage. Proper lubrication reduces friction and prevents metal-to-metal contact between moving parts, extending the engine’s lifespan.
C. Contaminant Management
The oil sump’s ability to collect contaminants helps keep the oil cleaner for longer. Clean oil is essential for optimal engine performance and efficiency, as it reduces the risk of engine deposits and sludge buildup.
D. Thermal Management
Effective cooling of the engine oil is crucial for maintaining its performance. The oil sump helps dissipate heat generated during engine operation, preventing overheating and ensuring the oil maintains its viscosity.
E. Ease of Maintenance
Having a centralized reservoir for oil makes maintenance tasks like oil changes easier. Technicians can quickly drain the oil from the sump, replace the oil filter, and refill the engine with new oil.
4. Types of Oil Sumps
A. Wet Sump System
The wet sump system is the most common configuration in modern vehicles. In this design, the oil sump is filled with oil, and the oil pump draws oil directly from the sump to circulate it throughout the engine. This system is straightforward and effective for most applications.
B. Dry Sump System
The dry sump system is typically used in high-performance engines, such as those found in race cars. In this design, the oil is stored in an external reservoir rather than the oil pan. A more complex oil pump system is used to draw oil from the reservoir and supply it to the engine. This system allows for better control of oil pressure and improved performance in high-demand situations.
C. Integrated Oil Sump
Some modern engines incorporate the oil sump into the engine block, creating a more compact design. This integration can reduce weight and improve efficiency but may complicate maintenance and repairs.
D. Modular Oil Sump
A modular oil sump is designed to allow for easier replacement or modification. This design is beneficial for vehicles that may require frequent upgrades or changes, such as racing vehicles.
5. Common Issues with Oil Sumps
A. Leaks
One of the most common issues with oil sumps is leaks. Over time, the gasket or seal between the sump and the engine block can wear out, leading to oil leaks. Leaking oil can create a mess, reduce the oil level, and potentially cause engine damage if not addressed.
B. Damage from Impact
The oil sump is located at the bottom of the engine and is susceptible to damage from road debris or obstacles. A damaged sump can lead to leaks and a loss of oil pressure, which can be detrimental to engine health.
C. Contaminant Buildup
While the oil sump helps filter contaminants, sludge and deposits can still accumulate over time. This buildup can restrict oil flow and reduce lubrication efficiency, leading to engine problems.
D. Oil Pump Failure
The oil pump is responsible for drawing oil from the sump and circulating it through the engine. If the pump fails, it can lead to insufficient oil flow, resulting in severe engine damage. The oil sump may be a contributing factor if the pump is not receiving adequate oil due to a clogged sump or low oil level.
6. Maintenance of the Oil Sump
A. Regular Oil Changes
Performing regular oil changes is one of the best ways to maintain the health of the oil sump and the engine. Fresh oil helps prevent sludge buildup and ensures optimal lubrication. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil change intervals.
B. Inspect for Leaks
Regularly inspect the oil sump and surrounding areas for signs of oil leaks. If you notice oil pooling beneath the vehicle or oil spots on the ground, have the sump and gasket checked for leaks.
C. Check Oil Level
Use the dipstick or oil level sensor to regularly monitor the oil level in the sump. Keeping the oil at the recommended level is crucial for proper lubrication and preventing engine damage.
D. Clean the Sump
If you notice sludge or debris buildup in the oil sump, consider cleaning it during an oil change. Remove the oil drain plug and allow the old oil to drain completely, then clean the sump with a suitable solvent before adding fresh oil.
E. Inspect the Gasket
During routine maintenance, inspect the oil sump gasket for signs of wear or damage. If you notice any cracks or deterioration, replace the gasket to prevent leaks.
F. Monitor Engine Temperature
Keep an eye on the engine temperature gauge while driving. If the engine is running hotter than normal, it may indicate a problem with oil circulation, which could be related to the oil sump. Address any overheating issues promptly.
7. Conclusion
The oil sump is a vital component of an internal combustion engine, serving as the reservoir for engine oil and playing a critical role in lubrication, cooling, and protection. Understanding the function and importance of the oil sump can help vehicle owners appreciate its role in maintaining engine performance and longevity.
Regular maintenance, including oil changes, leak inspections, and monitoring oil levels, is essential for ensuring the proper functioning of the oil sump and the engine as a whole. By taking care of this crucial component, drivers can enjoy better engine efficiency, reduced wear and tear, and a longer-lasting vehicle. Whether you’re a casual driver or a performance enthusiast, understanding the oil sump’s role can enhance your overall automotive knowledge and help keep your engine running smoothly for years to come.
Follow us on Facebook for more parts.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.