-6%
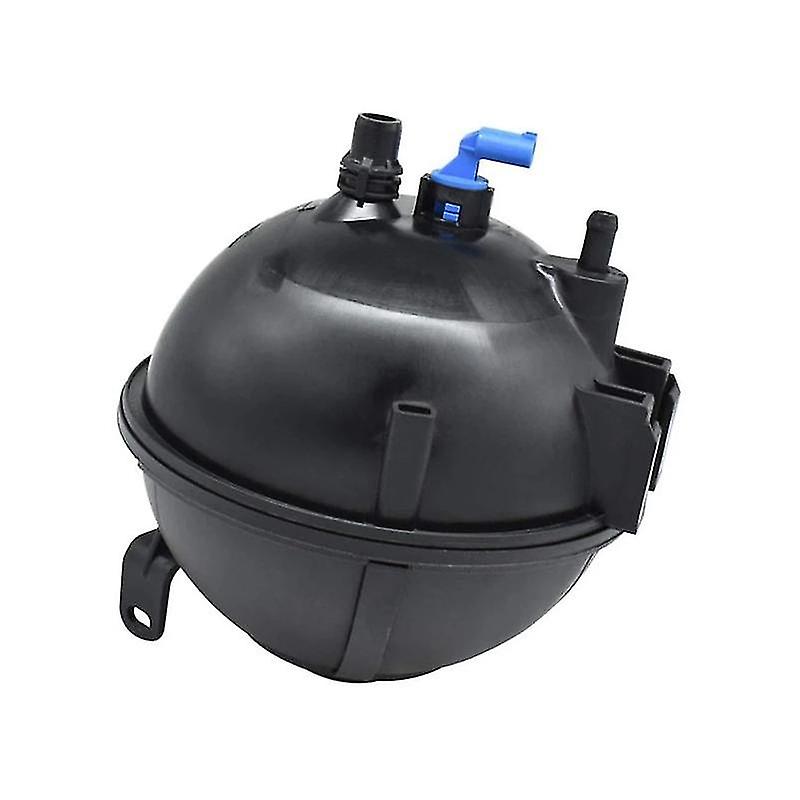
Get BMW X4 F26 Coolant Expansion Tank 17137639464 in Kenya
The coolant expansion tank, also known as a coolant reservoir or overflow tank, is an essential component of a vehicle’s cooling system. It plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature by accommodating the expansion and contraction of coolant. Without a properly functioning expansion tank, an engine could suffer from overheating, coolant loss, and long-term damage. In this detailed guide, we will explore the function, design, materials, importance, benefits, and maintenance of a coolant expansion tank.
1. What is a Coolant Expansion Tank?
A coolant expansion tank is a container designed to hold excess coolant that expands due to heat during engine operation. When the engine runs, the coolant heats up, expands, and is pushed into the tank. As the engine cools down, the coolant is drawn back into the cooling system, ensuring consistent fluid levels.
Unlike traditional overflow tanks, modern pressurized expansion tanks are integrated into the cooling system, making them an active component rather than just a passive reservoir.
2. Functions of a Coolant Expansion Tank
The expansion tank serves several critical functions in the cooling system:
a. Coolant Overflow Management
When coolant heats up, it expands and needs a place to go. The expansion tank captures this overflow, preventing coolant from spilling onto the ground or being lost from the system.
b. Air Separation and Bubble Removal
Air bubbles in the coolant can reduce cooling efficiency. The expansion tank helps remove trapped air, ensuring the coolant remains free of bubbles and improving heat transfer.
c. Maintaining Consistent Pressure
Modern coolant expansion tanks are pressurized, helping to maintain a stable system pressure. This increases the boiling point of the coolant, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation.
d. Preventing System Contamination
Since the expansion tank is a sealed unit, it prevents external contaminants like dirt and debris from entering the cooling system.
e. Allowing for Coolant Expansion and Contraction
Coolant expands when heated and contracts when cooled. The expansion tank accommodates these changes, preventing pressure fluctuations that could damage cooling components.
3. Design and Construction
a. Materials Used
Coolant expansion tanks are commonly made from the following materials:
- Plastic (Polypropylene, Polyethylene, or Nylon) – Lightweight, resistant to heat and corrosion, and cost-effective.
- Aluminum – Used in high-performance vehicles due to superior heat resistance and durability.
- Stainless Steel – Rare but used in specialized applications requiring extra durability.
b. Components of a Coolant Expansion Tank
A typical expansion tank consists of:
- Tank Body – Holds the coolant.
- Pressure Cap – Regulates pressure and acts as a safety valve.
- Coolant Level Sensor (in some models) – Alerts the driver when coolant levels are low.
- Inlet and Outlet Hoses – Connect the tank to the radiator and cooling system.
- Baffles or Dividers (in some designs) – Help reduce coolant sloshing and promote air separation.
4. Types of Coolant Expansion Tanks
a. Non-Pressurized Expansion Tanks
These tanks are simple overflow reservoirs. They collect excess coolant but do not play an active role in maintaining system pressure.
b. Pressurized Expansion Tanks
Found in most modern vehicles, these tanks are connected directly to the cooling system and help maintain consistent pressure. They allow coolant to circulate through the system even when stored in the tank.
c. Remote-Mounted Expansion Tanks
Some high-performance and heavy-duty vehicles use remotely mounted expansion tanks placed away from the radiator for better packaging and efficiency.
5. Importance and Benefits of a Coolant Expansion Tank
a. Prevents Overheating
By providing extra space for expanding coolant, the expansion tank helps prevent overheating and reduces strain on the radiator.
b. Extends Cooling System Lifespan
A properly functioning expansion tank prevents excessive pressure fluctuations, reducing wear on hoses, gaskets, and the radiator.
c. Reduces Coolant Loss
Without an expansion tank, excess coolant would be lost due to overflow. The tank ensures coolant is recovered and reused.
d. Helps Maintain Proper Coolant Levels
The tank provides a clear indication of coolant levels, allowing for easier monitoring and maintenance.
e. Improves Engine Performance
Maintaining optimal operating temperature enhances engine efficiency, fuel economy, and performance.
6. Common Issues with Coolant Expansion Tanks
a. Cracks or Leaks
Over time, plastic expansion tanks can develop cracks due to heat cycles and aging, leading to coolant leaks.
b. Clogged Hoses
Blockages in the hoses connecting the expansion tank to the radiator can prevent proper coolant flow, causing overheating.
c. Faulty Pressure Cap
A failing pressure cap can lead to improper pressure regulation, reducing cooling system efficiency and causing overheating.
d. Coolant Discoloration or Contamination
If the coolant appears rusty, oily, or sludgy, it may indicate contamination, which can clog the expansion tank and radiator.
e. Air Traps in the Cooling System
Improperly sealed expansion tanks can allow air into the system, reducing coolant effectiveness and increasing the risk of overheating.
7. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
a. Regular Inspection
- Check the coolant level regularly when the engine is cold.
- Inspect the tank for cracks, leaks, or discoloration.
- Ensure the hoses are firmly attached and free of leaks.
b. Flushing the Cooling System
Over time, coolant can degrade and accumulate debris. Flushing the system and replacing the coolant at manufacturer-recommended intervals prevents buildup.
c. Replacing the Expansion Tank
If the tank is cracked or leaking, replacement is necessary. It is recommended to use an OEM or high-quality aftermarket replacement to ensure proper fit and function.
d. Checking the Pressure Cap
A faulty pressure cap can cause coolant loss and overheating. Replacing it is a simple but crucial maintenance step.
e. Monitoring for Air Bubbles
If air bubbles are present in the coolant, bleeding the cooling system can help eliminate trapped air and improve efficiency.
8. How to Replace a Coolant Expansion Tank
If your coolant expansion tank is damaged, follow these steps for replacement:
- Let the Engine Cool Down – Never open the cooling system when the engine is hot.
- Drain the Coolant – Use a drain pan to catch the coolant.
- Disconnect Hoses and Sensor Wires – Remove clamps and detach the tank from the system.
- Remove the Old Tank – Unbolt and carefully take out the expansion tank.
- Install the New Tank – Secure it in place and reconnect hoses and sensors.
- Refill the Coolant – Use the recommended coolant type and fill to the proper level.
- Bleed the Cooling System – Remove any trapped air to ensure efficient cooling.
- Check for Leaks – Start the engine and observe for leaks or abnormal coolant levels.
9. Conclusion
The coolant expansion tank is an integral part of a vehicle’s cooling system, ensuring efficient heat management, preventing overheating, and maintaining consistent pressure. Regular inspection, timely maintenance, and proper coolant levels can significantly extend the lifespan of both the expansion tank and the entire cooling system. By understanding its function and maintaining it properly, you can ensure your vehicle operates at peak efficiency, reducing the risk of engine damage and costly repairs.
Follow us on Facebook for more parts.



Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.