-17%
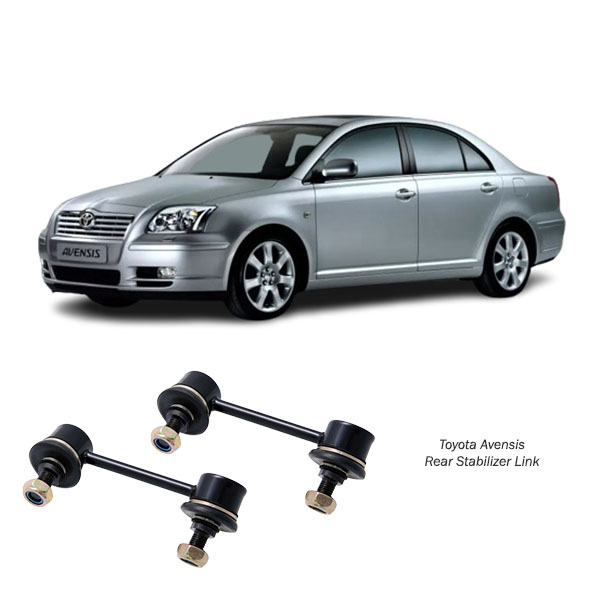
Get Toyota Avensis 250/255 Rear Stabilizer Link 0123-ARR in Kenya
The rear stabilizer link, also referred to as the sway bar link or anti-roll bar link, is a vital component in a vehicle’s suspension system. Its primary role is to connect the stabilizer bar (also known as the sway bar or anti-roll bar) to the suspension, ensuring stability and balance during cornering and uneven road conditions. This detailed guide explores the rear stabilizer link’s functions, benefits, maintenance, signs of wear, and replacement procedures, offering comprehensive insights for drivers, mechanics, and automotive enthusiasts.
1. Introduction to the Rear Stabilizer Link
a. What is a Rear Stabilizer Link?
The rear stabilizer link is a rod-like component with bushings or ball joints at each end. It connects the stabilizer bar to the rear suspension arms or struts. The stabilizer bar itself is a metal rod designed to reduce body roll by distributing forces across the vehicle’s suspension during turns.
b. Importance in Vehicle Dynamics
While the front stabilizer link is more commonly discussed due to its role in steering, the rear stabilizer link is equally important. It ensures that the rear wheels maintain grip and stability, enhancing overall control and reducing the risk of oversteer or understeer.
2. How the Rear Stabilizer Link Works
a. Connection to the Stabilizer Bar
The stabilizer link connects the stabilizer bar to the suspension arms or struts. It acts as a bridge, transferring forces between these components.
b. Force Distribution
When a vehicle turns, the outer wheels experience more force than the inner wheels. The stabilizer bar, through the stabilizer links, balances this force by transferring some of it from the outer wheels to the inner wheels, reducing body roll.
c. Enhanced Stability
This force transfer ensures that the vehicle remains level and stable, preventing excessive tilting or leaning during sharp turns or sudden maneuvers.
3. Materials and Construction
a. Common Materials
- Steel: Most stabilizer links are made of high-strength steel for durability and resistance to stress.
- Aluminum: Some vehicles use lightweight aluminum links for improved fuel efficiency.
- Composite Materials: Advanced stabilizer links may use composites for strength and reduced weight.
b. Components of the Link
- Ball Joints or Bushings: These allow the link to pivot and accommodate suspension movement.
- Protective Covers: Rubber or plastic covers shield the joints from dirt and moisture, extending their lifespan.
- Threaded Ends: These facilitate easy attachment to the stabilizer bar and suspension.
4. Benefits of the Rear Stabilizer Link
a. Improved Handling and Stability
By reducing body roll, the stabilizer link ensures better handling and a smoother driving experience, especially during cornering.
b. Enhanced Safety
Stable and balanced suspension minimizes the risk of accidents caused by loss of control during sharp turns or sudden lane changes.
c. Even Tire Wear
By distributing forces evenly across the suspension, the stabilizer link helps prevent uneven tire wear, extending tire lifespan.
d. Comfort
A well-functioning stabilizer link reduces vibrations and noise, enhancing passenger comfort on uneven or rough roads.
5. Signs of a Failing Rear Stabilizer Link
Recognizing early signs of failure is essential to maintain vehicle safety and performance. Common symptoms include:
a. Noise
- Clunking or Rattling Sounds: These noises, particularly from the rear of the vehicle, may indicate loose or damaged stabilizer links.
b. Poor Handling
- Increased Body Roll: Excessive leaning during turns can result from a worn or broken stabilizer link.
- Reduced Cornering Stability: Difficulty maintaining control during sharp turns is a key sign of stabilizer link issues.
c. Uneven Tire Wear
A failing stabilizer link can lead to uneven force distribution, causing tires to wear unevenly.
d. Visual Damage
- Cracked Bushings or Joints: Inspecting the link may reveal visible damage, such as cracks, rust, or loosened components.
6. Causes of Rear Stabilizer Link Wear
a. Age and Usage
Over time, constant exposure to stress, road vibrations, and environmental factors can wear out the stabilizer link.
b. Rough Road Conditions
Frequent driving on uneven or bumpy roads accelerates wear on the stabilizer link and its bushings.
c. Lack of Maintenance
Ignoring routine suspension inspections can lead to undetected damage and eventual failure of the stabilizer link.
d. Corrosion
Exposure to water, salt, and debris can cause rust and weaken the stabilizer link, particularly in regions with harsh winters.
7. Maintenance and Replacement
a. Regular Inspections
Routine suspension checks during vehicle servicing can identify early signs of wear and prevent further damage.
b. Cleaning
Keeping the stabilizer link and surrounding components clean reduces the risk of dirt and moisture buildup, which can cause corrosion.
c. Replacement Procedure
When the stabilizer link is worn or damaged, replacement is necessary. The process typically involves:
- Lifting the Vehicle: Securely lift the vehicle using a jack and stands to access the rear suspension.
- Removing the Old Link: Unscrew the bolts connecting the link to the stabilizer bar and suspension.
- Installing the New Link: Attach the new link to the stabilizer bar and suspension, tightening the bolts to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Testing the Vehicle: Lower the vehicle and test drive to ensure proper installation and improved handling.
d. Replacement Interval
Stabilizer links generally last 50,000 to 100,000 kilometers, but this can vary based on driving conditions and maintenance habits.
8. Choosing the Right Rear Stabilizer Link
a. Compatibility
Ensure the replacement link matches your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Consult the owner’s manual or a trusted mechanic.
b. Quality
Invest in high-quality stabilizer links from reputable brands to ensure durability and reliability.
c. OEM vs. Aftermarket
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Designed to match the vehicle’s original specifications.
- Aftermarket: May offer additional features or cost savings but require careful selection for compatibility.
9. The Role of Rear Stabilizer Links in Modern Suspension Systems
a. Integration with Advanced Suspension
In modern vehicles, stabilizer links are integrated with sophisticated suspension systems, such as adaptive dampers, to provide optimal stability and comfort.
b. Contribution to Vehicle Balance
The rear stabilizer link works in tandem with the front stabilizer link, ensuring balanced performance and consistent handling.
c. Essential for Performance Vehicles
High-performance and sports vehicles rely on robust stabilizer links to handle the stress of aggressive driving and sharp cornering.
10. Cost and Value
a. Cost of Replacement
The cost of rear stabilizer link replacement varies based on the vehicle model, labor charges, and the quality of the replacement part. Prices typically range from $50 to $150 per link.
b. Value of Timely Replacement
Timely replacement prevents damage to other suspension components, reducing overall repair costs and ensuring vehicle safety.
11. Conclusion
The rear stabilizer link is an indispensable part of the suspension system, ensuring stability, safety, and comfort. By connecting the stabilizer bar to the suspension, it reduces body roll and enhances handling, especially during turns and on uneven roads. Proper maintenance, timely inspections, and high-quality replacements ensure that this component performs effectively throughout its lifespan.
Whether you’re an everyday driver or an automotive professional, understanding the rear stabilizer link’s role can help you make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and upgrades. Its contribution to suspension performance highlights the importance of paying attention to even the smallest components in a vehicle, ensuring a safe and smooth driving experience.
Follow us on Facebook for more parts.