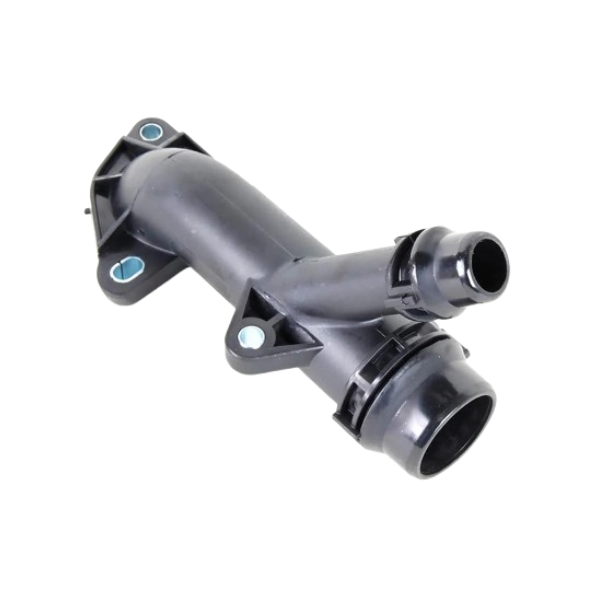
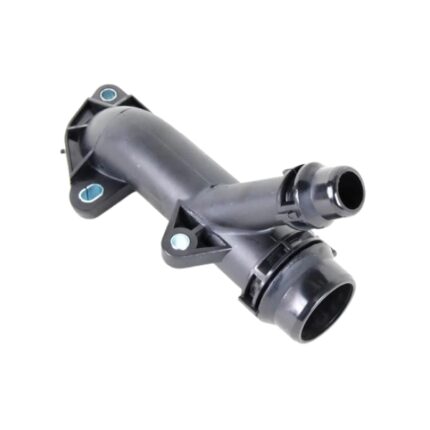
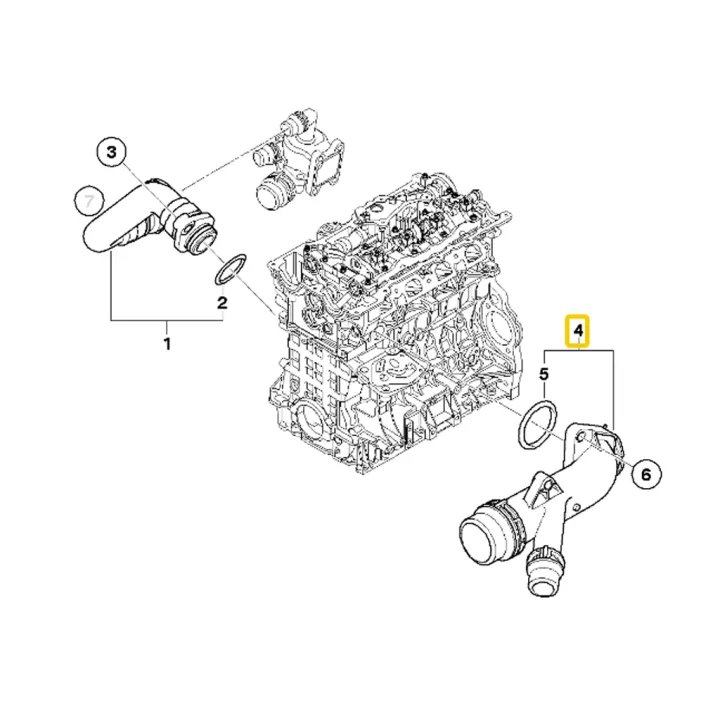
Get BMW E46 Water Coolant Flange 11537560130 in Kenya
The water coolant flange is a crucial component in a vehicle’s cooling system. Understanding its role, construction, and maintenance can help ensure optimal engine performance and longevity. Here’s an in-depth look at the water coolant flange:
1. What is a Water Coolant Flange?
A water coolant flange, sometimes referred to as a coolant flange or thermostat flange, is a component in the engine’s cooling system that connects various parts of the system and facilitates the flow of coolant. It acts as a junction point where coolant hoses and other components connect, allowing for the controlled distribution of coolant to different parts of the engine.
2. Function and Importance
2.1 Coolant Flow Management
The primary function of the water coolant flange is to manage the flow of coolant through the engine and cooling system. By directing coolant from the thermostat to the engine and radiator, it helps maintain the engine’s operating temperature. This regulation is critical for preventing overheating and ensuring that the engine runs efficiently.
2.2 Temperature Regulation
The flange also plays a role in temperature regulation by ensuring that coolant flows through the engine and radiator in the correct sequence. This helps the engine reach its optimal operating temperature and maintains it, which is essential for fuel efficiency and emissions control.
2.3 Integration and Connectivity
In many engines, the water coolant flange serves as a connection point for various hoses and components. This includes the thermostat housing, coolant temperature sensors, and coolant hoses that lead to the radiator and engine. Proper integration and secure connections are crucial for the cooling system to function effectively.
3. Construction and Materials
3.1 Materials Used
Water coolant flanges are typically made from materials that can withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion. Common materials include:
- Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for many modern engines.
- Plastic: Used in some newer vehicles due to its cost-effectiveness and resistance to corrosion, though it may be less durable compared to metal flanges.
- Cast Iron: Provides durability and strength but is heavier and more prone to rust.
3.2 Design Considerations
The design of the flange includes provisions for sealing, often incorporating O-rings or gaskets to prevent leaks. It also features mounting points for secure attachment to the engine or other components. The design must accommodate the various coolant hoses and sensors that connect to it.
4. Common Issues and Symptoms
4.1 Leaks
One of the most common issues with a water coolant flange is leaks. Over time, the flange or its seals may degrade, leading to coolant leaks. Symptoms of a leak include:
- Coolant Puddles: Finding coolant underneath the vehicle.
- Low Coolant Levels: Frequent need to top off the coolant reservoir.
- Overheating Engine: Insufficient coolant can cause the engine to overheat.
4.2 Cracks and Damage
Cracks or damage to the flange, especially in plastic models, can lead to coolant leaks and system failures. Symptoms include:
- Visible Cracks: Inspecting the flange may reveal visible cracks or damage.
- Engine Overheating: As the cooling system fails, the engine may overheat due to inadequate coolant flow.
4.3 Poor Connections
If the flange does not have secure connections, it can cause issues such as:
- Intermittent Leaks: Coolant may leak when the engine is running or when the vehicle is turned off.
- Inconsistent Temperature: Fluctuations in engine temperature due to poor coolant flow.
5. Maintenance and Replacement
5.1 Regular Inspection
Regular inspections of the coolant system, including the water coolant flange, are essential for early detection of potential issues. Check for signs of leaks, cracks, or wear and ensure that connections are secure.
5.2 Flange Replacement
If the flange shows signs of significant damage or wear, replacement may be necessary. The process typically involves:
- Draining Coolant: Remove coolant from the system to prevent spills during the replacement.
- Removing the Old Flange: Disconnect the hoses and remove any bolts or fasteners securing the old flange.
- Installing the New Flange: Position the new flange, secure it with bolts, and reconnect the hoses. Ensure that any seals or gaskets are properly aligned to prevent leaks.
- Refilling Coolant: Refill the cooling system with the appropriate type and amount of coolant.
- Testing: Start the engine and monitor for leaks or issues. Check the coolant levels and ensure proper engine temperature regulation.
6. Choosing the Right Flange
When selecting a replacement water coolant flange, consider the following:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the flange is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and engine type.
- Material Quality: Choose a flange made from durable, high-quality materials suitable for your vehicle’s operating conditions.
- OEM vs. Aftermarket: OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts are designed to match the specifications of the original component, while aftermarket parts may offer cost savings but vary in quality.
Follow us on Facebook for more parts.